AR vs XR: Key differences between Augmented Reality and Extended Reality explored
Contents
In recent years, the world of immersive technology has witnessed significant developments, generating interest and confusion surrounding various terms such as augmented reality (AR) and extended reality (XR).
- Augmented reality is a technology that superimposes computer-generated images on a user’s view of the real world, enhancing their experience by blending digital elements with the physical environment.
- On the other hand, extended reality encompasses a broader spectrum of immersive technologies, including augmented reality, virtual reality (VR), and mixed reality (MR).
As industries continue to explore different applications for these evolving technologies, understanding their distinctions and capabilities becomes crucial for users and developers alike. While AR adds digital information to the user’s environment, XR serves as an umbrella term that envelops the different ways we can merge or replace real-world experiences with computationally manipulated content, such as virtual and mixed reality technologies.
Key Takeaways
- Augmented reality enhances a user’s experience by overlaying digital elements on their view of the real world.
- Extended reality is an umbrella term for immersive technologies, including AR, VR, and MR.
- Understanding the capabilities and differences between AR and XR is essential for the technology’s users and developers.
Understanding the Spectrums of Reality
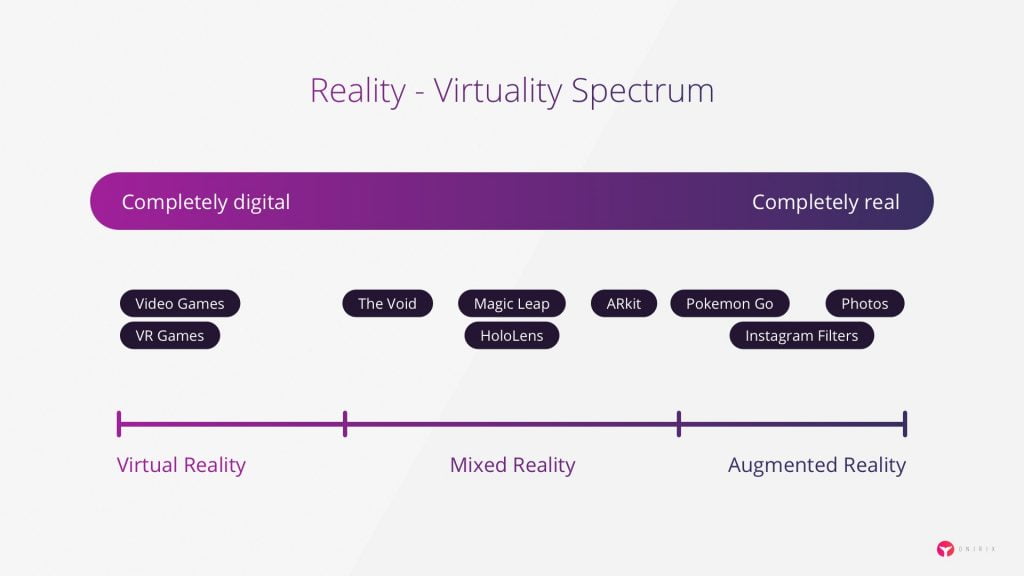

Augmented Reality (AR)
Augmented reality is a technology that enhances our perception of the real world by overlaying computer-generated information or visuals on top of it. With AR, users can still see and interact with the real environment while receiving additional context through digital overlays. This can be achieved using smartphones, tablets, or smart glasses, adding a layer of interactivity and information to our surroundings. Examples of AR applications include navigation apps that provide directions on the screen, overlaying them on the real world, and gaming experiences like Pokémon Go.
Extended Reality (XR)
Extended reality is an umbrella term that encompasses all of the above technologies – AR, VR, and MR – as they continue to evolve and interact with one another. XR covers the entire spectrum of reality technologies, from fully real to fully virtual environments and everything in between. This broad definition allows for the development and integration of various immersive experiences, whether they involve augmenting our perception of the real world, transporting users into entirely digital realms, or blending elements of both to create interactive mixed reality environments. As technology progresses, we can expect the lines between these spectrums to blur even further, making way for more innovative and immersive experiences in the future.
Comparison Table
Aspect | Augmented Reality (AR) | Extended Reality (XR) |
|---|---|---|
Immersion | AR integrates virtual elements into the real world, enhancing the user’s perception of their surroundings. | XR offers varying levels of immersion, from complete virtual environments to hybrid experiences that merge virtual and real elements. |
Usage | AR is commonly used in mobile devicesor as web AR allowing users to interact with digital content in their real-world environment without the need for specialized equipment. | XR technologies are often used with wearables such as headsets and devices, providing a more comprehensive and encompassing digital world that goes beyond augmenting reality. |
Applications | AR has a wide range of applications, including gaming, education, design, healthcare, and more. It’s often used to overlay informative content onto real-world objects, fostering a learning experience tailored towards user engagement. | XR encompasses the applications of AR, VR, and MR, and is used in fields like education, healthcare, military training, marketing, remote working, and more. It’s designed to create immersive experiences that can be interactive and dynamic. |
Key Technology Components
Headsets and Glasses
One of the most crucial components in both augmented reality (AR) and extended reality (XR) experiences are the headsets and glasses used to view and interact with digital content. AR smart glasses and XR headsets come in various forms, ranging from smartphone-compatible devices to standalone headsets with built-in processors. These devices allow users to see digital content overlaid on their physical environment or experience fully immersive virtual worlds, depending on the specific application.
Some popular examples of headsets and glasses include AR glasses like Microsoft HoloLens and Google Glass, as well as VR headsets such as Oculus Rift and HTC Vive. These devices use a combination of high-resolution displays, cameras, and sensors to track users’ movements and provide a seamless, immersive experience.
Camera and Screen
The camera and screen are essential components in AR and XR experiences, as they are responsible for capturing the real-world environment and projecting the digital content onto the user’s field of view. Typically, AR and XR devices use one or more cameras to track the user’s position and environment, while the screen or display projects the digital content in real-time. In AR applications, the camera is used to overlay digital elements onto the physical world, creating a blended environment where real and virtual objects coexist. On the other hand, XR experiences often involve a more dynamic interaction between physical and virtual elements, allowing users to affect or manipulate digital content directly.
Smartphone-based AR and XR experiences also rely on the device’s built-in camera and screen to display digital content. For example, popular mobile AR applications like Pokémon Go and Snapchat utilize the smartphone’s camera and display to create immersive experiences for users on the go.
Processor
The processor is the brain behind AR and XR experiences, responsible for rendering digital content, tracking users’ movements, and managing the overall performance of the system. AR and XR devices often use powerful processors to ensure a smooth, lag-free experience as users interact with digital content.
Some headsets, like the standalone Oculus Quest, have built-in processors that enable them to run without the need for an external computer, offering users a more portable and convenient option for experiencing AR and XR. Meanwhile, smartphone-based applications heavily rely on the processing power of the mobile devices to provide real-time tracking, positioning, and rendering of digital content within the physical environment. Advanced processors in modern smartphones help deliver a seamless and immersive AR and XR experience for users, allowing them to enjoy these technologies in a convenient and accessible manner.
Experiencing Different Realities
Gaming
In the world of gaming, both augmented reality (AR) and extended reality (XR) provide unique and immersive experiences for players. AR games, such as Pokémon GO, integrate digital elements into the real world, allowing players to interact with their surroundings in a new way. On the other hand, XR encompasses various immersive technologies, including AR and virtual reality (VR), resulting in a broader range of gaming experiences.
Movies
The entertainment industry has also embraced AR and XR technology to create immersive movie experiences. AR movies enhance the viewer’s experience by displaying additional information or interactive elements on top of the film. XR technology, which includes VR, allows moviegoers to step into the world of the film, creating a first-person perspective and heightened sense of immersion.
Education
In education, both AR and XR play a crucial role in enhancing learning experiences for students. AR applications can provide additional information or visualizations to supplement traditional teaching methods, while XR technologies can create virtual environments for students to explore and learn from. For example, medical students can use XR applications to simulate surgeries and gain hands-on experience before entering the operating room.
Healthcare
Healthcare is another field that benefits from the advancements in AR and XR technology. Medical professionals can use AR applications to overlay digital information onto a patient’s body, such as real-time vital signs and diagnostic data, improving accuracy during procedures. XR technology offers a broader range of applications, including virtual therapy sessions and immersive training for healthcare staff.
Retail and Shopping
In the retail and shopping sectors, AR and XR technologies enhance the user experience by offering immersive and personalized shopping experiences. AR applications enable customers to visualize products in their environment, such as placing virtual furniture in their home, or to access product information simply by scanning the item. XR, being a more all-encompassing technology, can offer virtual shopping experiences, allowing users to navigate through virtual stores and interact with products in entirely digital environments.
Specific Tools and Applications
Microsoft Hololens
Microsoft Hololens 1 is an impressive mixed reality (MR) headset that enables users to interact with both the physical and digital world simultaneously. The Hololens 2, its latest iteration, has come with improved features, such as a larger field of view and advanced gesture controls, making it more suitable for industries like engineering, manufacturing, and healthcare.
Oculus Rift
The Oculus Rift 2 is a virtual reality (VR) headset that fully immerses its users in a digital environment. It has been a breakthrough in the gaming industry, providing an immersive experience through high-quality visuals and a wide range of compatible games. The Oculus Rift is also finding applications in fields like healthcare, architecture, and virtual training simulations.
Pokémon Go
Pokémon Go is a popular mobile game that utilizes augmented reality (AR) technology to overlay digital elements onto the real world. Using their smartphones, players can locate, capture, and train virtual creatures, known as Pokémon, in their physical surroundings. Pokémon Go’s success has showcased the mass appeal of AR technology and opened up new opportunities for AR-based applications.
Ikea Place
Ikea Place is an AR app that allows users to virtually place furniture from the Ikea catalog into their homes. By overlaying 3D models of furniture onto a smartphone’s camera view, the app helps users visualize how products would fit within their existing spaces. Ikea Place has greatly improved the shopping experience and has become a prominent example of the potential for AR technology in the retail industry.
Google Glass
Google Glass 3 is an early example of AR-infused wearable technology. The device was designed to resemble a pair of glasses, featuring a small screen in front of the wearer’s eye that provides real-time information and augmented content. While the initial version was met with mixed reviews, Google has since pivoted to focus on enterprise applications, such as remote collaboration and hands-free data access for workers in various industries.
The Future of Extended Realities
Metaverse
The metaverse 4 is an emerging concept often discussed in the context of extended realities. It refers to a shared, immersive digital space that combines elements of both the real-world environment and the virtual world, blurring the lines between physical and digital experiences. As extended realities (XR) continue to evolve, the metaverse will likely be shaped by three key technologies: virtual reality (VR), augmented reality (AR), and brain-computer interfaces.
In the metaverse, users can interact, socialize and work together in this intertwined digital-physical landscape. The potential of the metaverse has been apparent for years and was first popularized in science fiction books such as “Ready Player One.” With developments in spatial computing and XR technology, we are now witnessing some of the foundational building blocks that will help bring the metaverse concept to life.
Social Media
Social media platforms are also keen to explore and leverage the capabilities of extended realities. By introducing AR and VR elements into their ecosystems, social media can provide users with more engaging, interactive experiences. For example, platforms may soon offer the option to virtually try on clothes or accessories before purchasing, participate in 3D virtual events, or share immersive, 360-degree content.
The integration of extended reality technologies into social media platforms is expected to transform the way we communicate, share experiences, and consume content, enhancing user experiences in novel ways throughout the social media landscape.
Military
The military has long been interested in harnessing the potential of extended reality technologies for various applications. For instance, it uses VR, AR, and MR for training purposes, providing troops with realistic simulations of battlefield scenarios, and helping them develop essential skills in a controlled environment. Furthermore, these technologies can be utilized for medical training, enabling personnel to gain practical experience without the need for real-world dissections or surgeries.
Beyond training, extended reality technologies have the potential to enhance situational awareness on the battlefield. Soldiers can use AR-equipped devices to access digital overlays on real-world environments, directing them to landmarks, objectives, or even enemy forces. As the umbrella term encompassing VR, AR, and MR, XR will likely play a pivotal role in the military’s efforts to innovate and expand its capabilities in the coming years.
What are the key differences between AR and XR?
Augmented Reality (AR) is a technology that overlays digital information onto a user’s real-world environment, whereas Extended Reality (XR) encompasses a range of immersive technologies, including AR, Virtual Reality (VR), and Mixed Reality (MR). While AR adds digital elements to the real world, XR technologies aim to create entirely immersive experiences. AR, VR, MR, and XR each have different purposes and underlying technologies.
How do AR and XR applications impact various industries?
Both AR and XR applications revolutionize industries by offering immersive, interactive experiences. In the healthcare industry, AR and VR devices can help professionals during surgical procedures and patient consultations. Retail businesses can leverage AR for product visualization, while XR technologies provide immersive training experiences in construction, manufacturing, and aviation sectors.
Which industries commonly utilize XR technologies?
Industries that heavily utilize XR technologies include entertainment, gaming, healthcare, education, real estate, retail, and manufacturing. Growth in the XR market is driven by advancements in hardware and software, which expand applications across domains.
What are some popular AR, VR, and MR examples?
For AR, examples include the popular gaming app Pokémon GO and IKEA Place, an app that allows users to visualize furniture in their homes. VR examples include the Oculus Rift headset, which is popular for gaming and immersive experiences. As for MR, Microsoft’s HoloLens combines elements of AR and VR to provide a seamless interaction between digital and physical worlds.
How do AR and XR technologies differ in user experience?
AR enhances the real world with digital elements that users can interact with through their devices. It keeps them grounded in their surroundings and supports practical applications. In contrast, XR technologies, such as VR and MR, aim to create entirely immersive experiences, often isolating the user from their physical environment as they engage with digital content. These experiences may be more suitable for entertainment, training, and virtual collaboration.
What is the future potential of AR, VR, and XR in the metaverse?
The burgeoning concept of the metaverse, a digital space that converges real and virtual worlds, holds immense potential for AR, VR, and XR technologies. As XR plays a fundamental role in the metaverse, it is expected to drive advancements in hardware, software, and infrastructure. The integration of these technologies will enable broader applications, from social interaction to commerce, and redefine the way people live, work, and play.

